How to Read Tidal Charts for Surf Fishing
Surf fishing is an exhilarating way to connect with the ocean and catch a variety of fish species. Success in this sport relies heavily on understanding the environment, particularly the tides. Tidal charts are essential tools for surf anglers, providing critical information about tide movements that influence fish behavior. By learning to read these charts, you can time your fishing trips to maximize your chances of a great catch. This guide, brought to you by Crazy Fishing Gear, will walk you through the process of reading tidal charts, ensuring you’re well-equipped for your next surf fishing adventure.
Understanding Tidal Charts and Their Importance
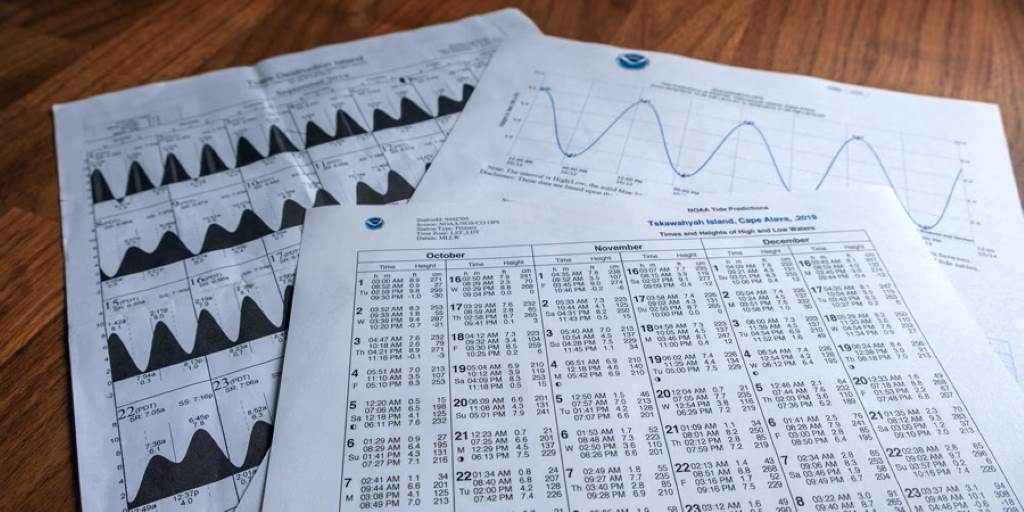
Tidal charts display the predicted times and heights of high and low tides for specific locations. These charts are generated using data from coastal monitoring stations and are available through various sources, such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) or local fishing apps. For surf fishing, tides dictate when fish are most active, as water movement stirs up baitfish and creates feeding opportunities. Knowing how to interpret these charts helps you plan your fishing around optimal conditions. For instance, many anglers prefer fishing during incoming tides, as fish tend to move closer to shore to feed. Additionally, understanding your gear, such as what is a reel box, can enhance your setup, ensuring your equipment is ready for tidal conditions.
Tides are influenced by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun, resulting in daily cycles of high and low tides. Typically, coastal areas experience two high tides and two low tides every 24 hours and 50 minutes, known as a tidal day. Tidal charts provide precise timings for these events, along with tide heights, which indicate the vertical water level relative to a reference point, often mean lower low water (MLLW). By studying these charts, you can identify patterns that align with fish activity, making your fishing trips more productive.
Key Components of a Tidal Chart
To read a tidal chart effectively, you need to understand its main elements. Here’s a breakdown of what to look for:
- High Tide and Low Tide Times: These are the moments when the tide reaches its peak (high tide) or its lowest point (low tide). The chart lists specific times for each event, usually in a 24-hour format.
- Tide Heights: Expressed in feet or meters, this indicates how high or low the water level will be compared to the reference point. Positive numbers represent high tides, while negative numbers may indicate extremely low tides.
- Tidal Range: This is the difference in height between high and low tides. A larger tidal range often means stronger currents, which can influence fish behavior.
- Moon Phases: Some charts include moon phase information, as tides are stronger during full and new moons (spring tides) and weaker during quarter moons (neap tides).
By familiarizing yourself with these components, you can quickly interpret a tidal chart and make informed decisions about when and where to fish.

Step-by-Step Guide to Reading a Tidal Chart
Reading a tidal chart may seem daunting at first, but with practice, it becomes second nature. Follow these steps to get started:
- Locate the Chart for Your Fishing Spot: Find a tidal chart specific to your fishing location. NOAA’s tide prediction tool (tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov) is an excellent resource for accurate, location-specific data. Alternatively, apps like Tides Near Me or FishWeather provide user-friendly interfaces.
- Identify High and Low Tide Times: Check the chart for the times of high and low tides on the day you plan to fish. Note the exact times and whether they align with sunrise or sunset, as these periods often yield the best results.
- Assess Tide Heights: Look at the tide heights to gauge the water level. For example, a high tide with a height of 5 feet means the water will be deeper, potentially bringing fish closer to shore.
- Evaluate the Tidal Range: Calculate the difference between high and low tide heights. A larger range may indicate stronger currents, which can attract predatory fish but may also make casting more challenging.
- Consider Moon Phases: If the chart includes moon phase data, note whether it’s a spring or neap tide. Spring tides, occurring during full or new moons, create stronger currents and are often ideal for surf fishing.
Once you’ve gathered this information, plan your fishing around the incoming tide (rising water) or the outgoing tide (falling water), as these periods often trigger feeding activity. For example, the hour before and after high tide is typically productive, as fish move into shallower waters to hunt.
How Tides Affect Surf Fishing
Tides play a critical role in surf fishing by influencing water movement, baitfish distribution, and fish behavior. During an incoming tide, water pushes baitfish toward the shore, attracting larger predatory fish like striped bass or red drum. Conversely, outgoing tides can create rip currents and troughs where fish congregate to ambush prey. However, fishing during slack tides—when the tide is neither rising nor falling—may be less productive, as water movement is minimal, and fish are less active.
Additionally, the tidal range affects where fish are located. A larger tidal range can expose sandbars or create deeper channels, altering the best spots to cast. For instance, during low tide, you might target troughs or drop-offs where fish gather, while high tide allows you to fish closer to the shore. Understanding these dynamics helps you choose the right time and location for your casts.
Tips for Using Tidal Charts Effectively
To make the most of tidal charts, consider these practical tips:
- Combine with Weather Data: Tides are just one piece of the puzzle. Check wind conditions and barometric pressure, as they also influence fish behavior. Websites like weather.gov provide reliable forecasts.
- Focus on Transition Periods: The hours around high and low tides are often the most productive. Plan to arrive at your fishing spot an hour before the tide peaks or dips.
- Adapt to Local Conditions: Each beach has unique features, such as sandbars or jetties, that interact with tides. Observe how tides affect your specific spot over multiple trips.
- Use Technology: Apps and GPS-enabled devices can provide real-time tide data, making it easier to stay updated on the go.
By integrating tidal chart data with local knowledge and weather conditions, you can refine your surf fishing strategy and increase your success rate.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced anglers can misinterpret tidal charts. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for:
- Ignoring Local Variations: Tide times and heights can vary significantly even within a few miles. Always use a chart specific to your fishing location.
- Overlooking Moon Phases: Failing to account for spring or neap tides can lead to poor timing, as fish activity varies with tidal strength.
- Focusing Solely on High Tide: While high tide is often productive, outgoing tides can also be excellent, especially for species that feed in rip currents.
By avoiding these mistakes, you’ll be better equipped to use tidal charts effectively and improve your surf fishing outcomes.
Read Also: How to Stay Balanced and Confident on Your Board
FAQs
Why are tidal charts important for surf fishing?
Tidal charts help anglers predict when fish are most active by showing high and low tide times, which influence water movement and baitfish distribution.
What is the best tide for surf fishing?
Incoming tides are often best, as they push baitfish toward shore, attracting predatory fish. However, outgoing tides can also be productive in areas with strong currents.
How do moon phases affect tides?
Full and new moons cause spring tides with stronger currents, while quarter moons result in neap tides with weaker currents, affecting fish behavior.
Where can I find reliable tidal charts?
NOAA’s tide prediction tool (tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov) and apps like Tides Near Me offer accurate, location-specific tidal data.
How do I choose the right fishing spot based on tides?
Look for areas with structure, like sandbars or troughs, that are influenced by tides. High tides allow fishing closer to shore, while low tides expose deeper channels.
Conclusion
Reading tidal charts is a fundamental skill for successful surf fishing. By understanding high and low tide times, tide heights, and tidal ranges, you can time your trips to coincide with peak fish activity. Combining tidal data with weather forecasts and local knowledge enhances your ability to find the best fishing spots. With practice, you’ll be able to interpret tidal charts confidently, making every surf fishing trip more rewarding. So grab your gear, check the tides, and hit the beach for an unforgettable fishing experience.