What’s the Deal with HSA Investment Options?

Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) have become increasingly popular in recent years as a way for individuals to save for medical expenses while enjoying tax benefits. However, what many people don’t realize is that HSAs can be used not just as a savings account but also as an investment vehicle. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of HSA investment options, exploring how they work, their benefits, and important considerations for anyone looking to make the most of their HSA.
Understanding HSAs: A Quick Recap
Before we jump into HSA investments, let’s briefly recap what an HSA is. An HSA is a tax-advantaged savings account available to individuals enrolled in high-deductible health plans (HDHPs). Contributions made to an HSA are tax-deductible, and the funds can be used for qualified medical expenses, such as doctor’s visits, prescriptions, and more.
Are you looking for an effective way to save for medical expenses? Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) may be just what you need. One of the key benefits of HSAs is their triple tax advantage: contributions are tax-deductible, earnings grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. However, it’s crucial to keep in mind that i accidentally used my hsa card for groceries. It can result in penalties and taxes on those transactions. To steer clear of any issues with the IRS, make sure to carefully track your HSA expenses and only use the funds for qualified medical expenses.
The Basics of HSA Investment Options
1. HSA Investment Account
Most HSAs come with an option to open an investment account alongside the basic savings account. This investment account allows you to invest your HSA funds in various financial instruments, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. It’s a way to potentially grow your HSA balance over time.
2. Risk and Reward
Investing always comes with a level of risk. While an HSA investment account offers the potential for higher returns compared to a traditional savings account, it also carries the risk of market fluctuations. It’s essential to consider your risk tolerance and investment goals when deciding how to allocate your HSA funds.
3. Tax Advantages of HSA Investments
One of the key advantages of HSA investments is the tax benefits they offer. Just like the HSA savings account, the earnings on your investments within the HSA are tax-free, provided they are used for qualified medical expenses. This tax-free growth can significantly boost your long-term savings.
Choosing the Right HSA Investment Options
4. Assess Your Risk Tolerance
Before you start investing your HSA funds, it’s crucial to assess your risk tolerance. Consider how comfortable you are with the potential ups and downs of the market. If you have a low risk tolerance, you may opt for more conservative investment options.
5. Diversification
Diversifying your HSA investments is a fundamental strategy for managing risk. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, you can reduce the impact of a downturn in any single investment.
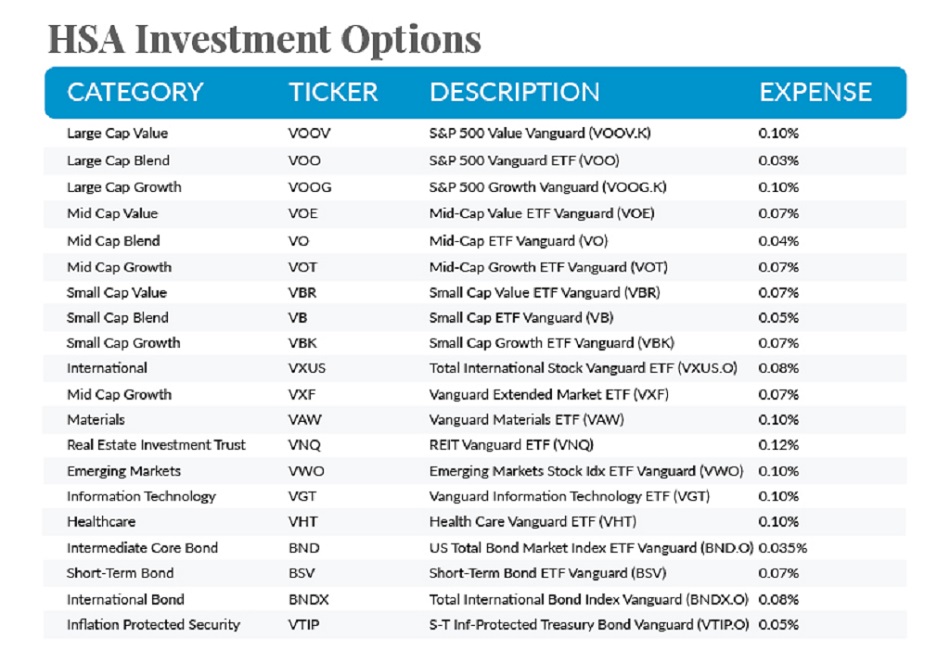
6. Investment Options
HSAs typically offer a range of investment options, including low-cost index funds, target-date funds, and individual stocks and bonds. Each option has its own level of risk and potential return, so it’s essential to research and choose investments that align with your financial goals.
Benefits of HSA Investments
7. Potential for Growth
One of the most significant advantages of HSA investments is the potential for your savings to grow significantly over time. Unlike a regular savings account, which offers minimal interest, investing in stocks and bonds can lead to substantial returns.
8. Triple Tax Benefits
It’s worth emphasizing that HSA investments continue to enjoy the triple tax benefits of contributions, tax-free growth, and tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses. This makes HSAs a powerful tool for both healthcare savings and retirement planning.
9. Long-Term Savings
HSA investments are not just for short-term medical expenses. They can serve as a vehicle for long-term savings, helping you build a substantial nest egg for retirement healthcare costs.
Considerations and Cautions
10. Fees and Expenses
While HSA investments can offer great rewards, it’s essential to be aware of any fees and expenses associated with the investment options. High fees can eat into your returns, so choose investments wisely.
11. The Opportunity Cost
Every dollar you invest in your HSA is a dollar that won’t be immediately available for medical expenses. Consider your current health needs when deciding how much to invest.
12. Keep an Eye on Contribution Limits
HSA contributions are subject to annual limits set by the IRS. It’s essential to stay within these limits to maintain your HSA’s tax-advantaged status.
In conclusion, HSA investment options provide a unique opportunity to grow your healthcare savings and prepare for future medical expenses. Payroll Services play a crucial role in ensuring employee financial security, and by understanding the basics, assessing your risk tolerance, and choosing the right investments, you can make the most of your HSA’s potential for long-term financial well-being. Remember that the triple tax benefits make HSAs a valuable tool for both short-term and long-term financial goals.
FAQs
- Can I invest my entire HSA balance?
No, there may be a minimum balance requirement for investing your HSA funds. Check with your HSA provider for specific details.
- Are HSA investments FDIC-insured?
No, HSA investments are not FDIC-insured. They carry market risk, and your investments may go up or down in value.
- Can I use HSA investments for non-medical expenses?
Yes, but keep in mind that non-medical withdrawals will be subject to income tax and a 20% penalty if you’re under 65.
- How do I change my HSA investment allocation?
You can typically adjust your HSA investment allocation through your HSA provider’s online portal or by contacting their customer support.
- Are HSA contributions tax-deductible?
Yes, contributions made to your HSA are tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income for the year.